What is an NFT and How Does It Work?
NFT (Non-Fungible Tokens) are special digital assets that differ from other tokens (for example, cryptocurrencies) in their uniqueness and indivisibility. Although the technology for assigning uniqueness to digital assets was developed around 2016, a surge of interest in the NFT market occurred in 2020-2021, during the period of growing popularity of the first tokens with digitized music and art.
You don’t have to be involved in art to create an NFT. It can be made by any Internet user, and then sold on a special platform – the NFT exchange. In addition to various fields of art, NFTs are actively used in metaverses, GameFi projects, and even in copyright registration.
The Technology Behind NFTs
NFT tokens cannot be created without using the blockchain. Let’s delve into the technical part and figure out how NFTs differ from other tokens and how they relate to cryptocurrency.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
The first NFTs were created using Ethereum blockchain with smart contracts of the ERC-721 or ERC-1155 standards. However, due to the high cost of gas, the tokens were very expensive. Today, it is possible to create NFTs in a more cost-effective way on various blockchains. Among the Ethereum alternative networks are: Polygon, BNB Chain, Polkadot and Cosmos.
The two main characteristics of NFTs are uniqueness and indivisibility. These properties distinguish non-fungible tokens from cryptocurrencies, where each coin is equivalent to another coin (non-unique) and may have fractional parts (such as satoshis in BTC).
- Uniqueness is ensured by a special digital signature of the NFT token. Such a signature cannot be replaced or copied, which helps preserve the authorship of the token creator;
- Indivisibility ensures the integrity of the token.
Ensuring Uniqueness and Ownership
The authorship of an NFT token is fixed at the creation stage, and no one has the ability to change it, even if the token itself has been sold several times. Using blockchain technology, it is possible to track the history of the transfer of a token from the moment of its creation. A digital signature ensures that the authorship of the token creator remains with him, and the right to dispose of the NFT is transferred to whoever currently owns the token (for example, if it was purchased from the author).
The Appeal of NFTs
The NFT market is considered to be highly volatile and speculative. The most popular at modern stage of its development are art and musical works (games with metaverses are also gradually gaining interest). Because of this fact, main market participants are traders, collectors and artists.
For example, singer and artist Grimes sold a collection of 10 NFT tokens with video and art for $6 million in 2021. Among the most expensive NFTs to date is Everyday’s: The First 5000 Days by artist Beeple. A token of just one collage was sold for $69.34 million.
Rare NFT music albums are also popular. For example, the album Ultraviolet by American DJ 3LAU was released in 33 copies and sold for $11 million.
One of the largest acquisitions in the metaverse sector was a plot of land in The Sandbox, which was sold in 2021 for $4.3 million.
How to Create and Sell an NFT
You don’t have to be a popular musician or famous artist to make (mint) and sell an NFT. It is enough to know the sequence of steps to create a token and have a crypto wallet connected to a minting service (for example, to an NFT marketplace). Let’s look at the process of creating an NFT using the example of the Metamask wallet and the Opensea NFT marketplace.
1. Create a Wallet and Connect to OpenSea
- Go to official website Metamask and download the wallet by clicking Download on the main page;
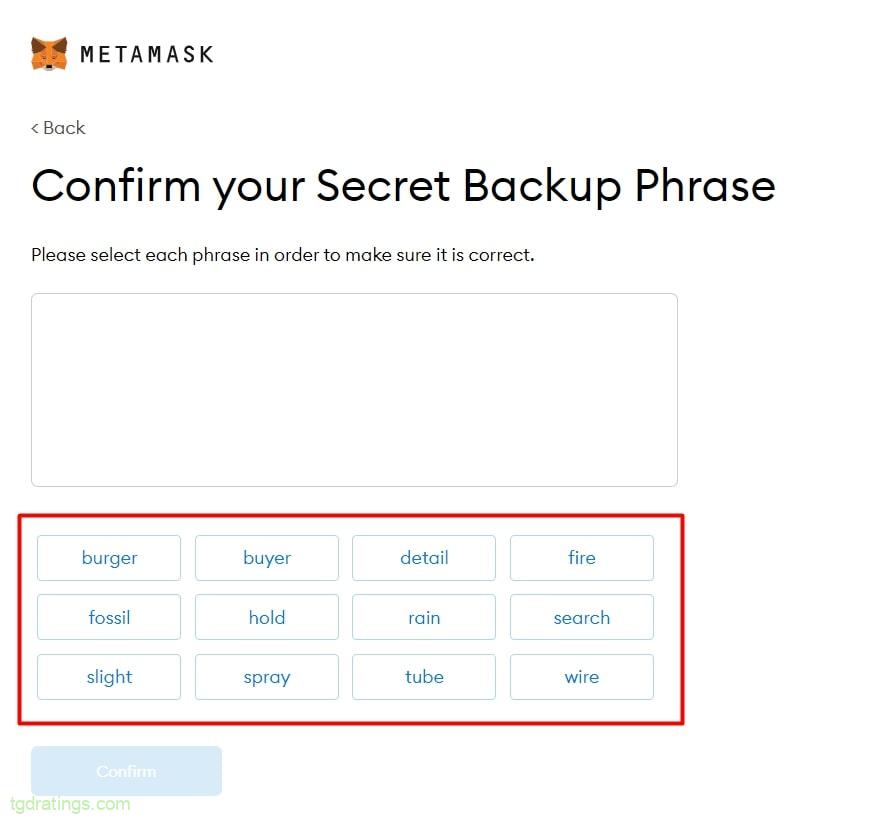
Metamask mainpage - Create a new wallet by clicking Create new wallet, create a password and generate a 12-word seed phrase (be sure to save it in a safe place);
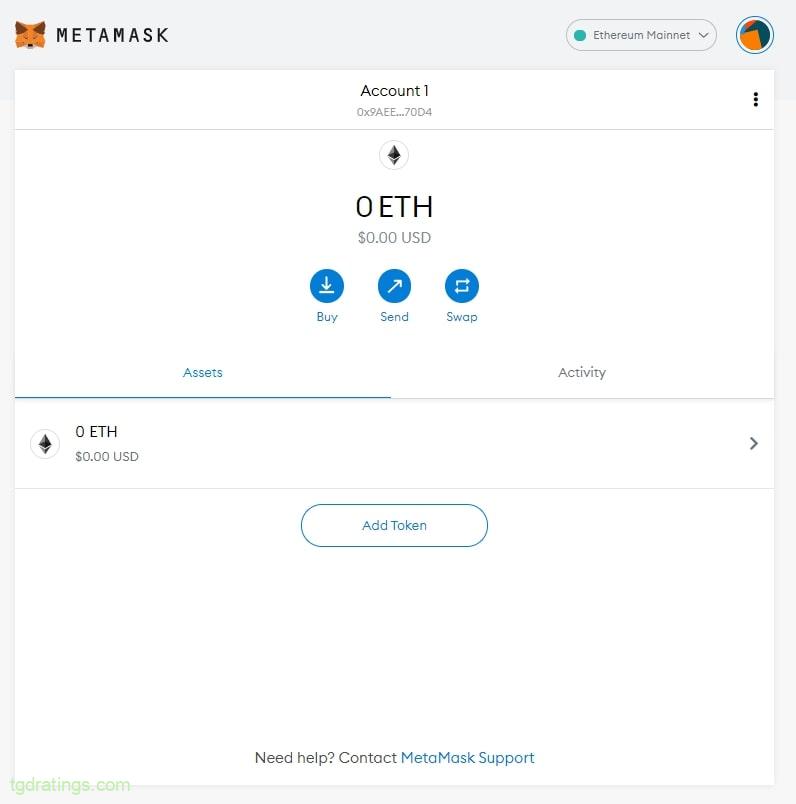
Confirmation of the created seed phrase - If the wallet was created successfully, a welcome screen will appear;
Metamask welcome screen - The Ethereum network is automatically added to the new wallet by default. To pay lower commission for creating NFTs on OpenSea, you need to connect the Polygon (MATIC) wallet as an additional network;
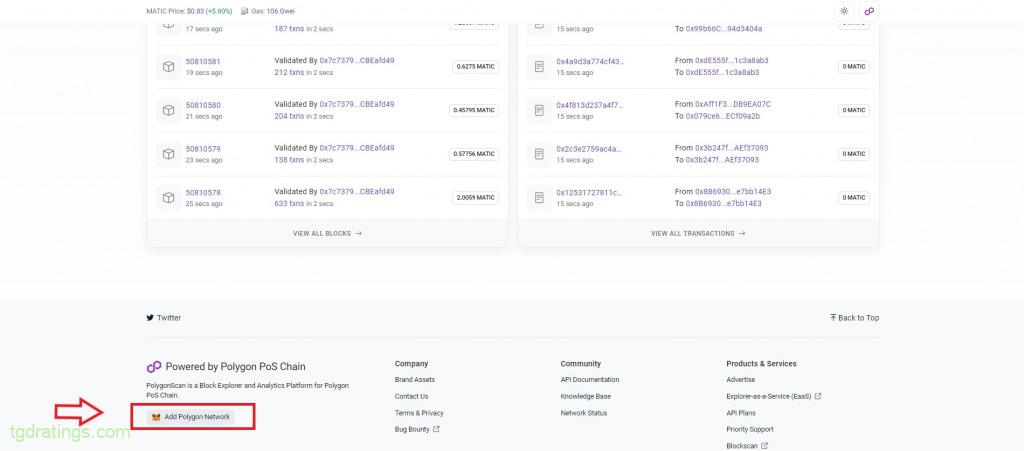
Interface of new Metamask wallet - To automatically add the Polygon network to Metamask, go to polygonscan.com → scroll main page down → click Add Polygon Network → confirm the connection in the wallet;
Automatic connection to the Polygon network - Make sure that Polygon network is active in your wallet → click Buy → indicate the country and select one of the available replenishment methods → replenish your wallet with MATIC coins;
- Connect your wallet to the Opensea service. To do this, go to official website and click Login → from the list wallets, select Metamask → confirm the subscription in the wallet.
OpenSea homepage
2. Create your own NFT
After creating a wallet and connecting it to the Opensea marketplace, you can begin creating your first NFT token. For this:
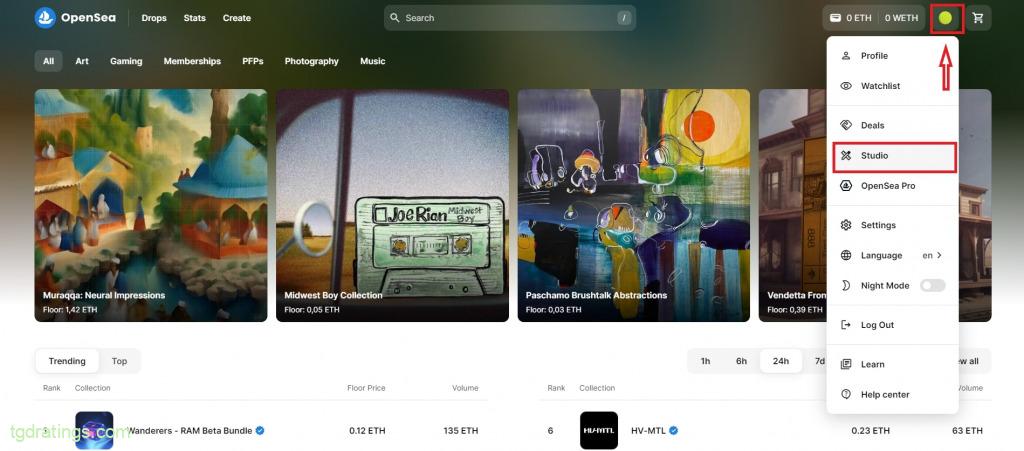
- Click on the user profile icon → Studio → Create → Mint an NFT;
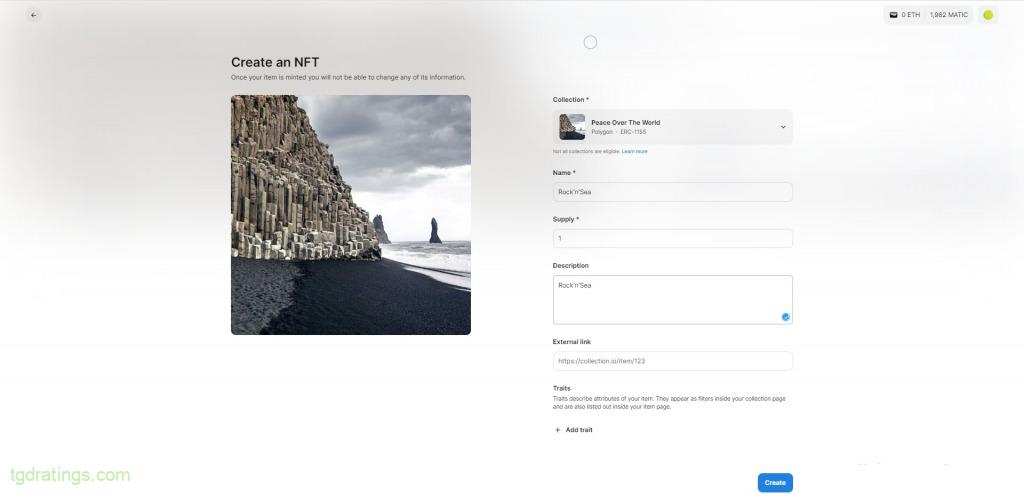
NFT creation menu - Upload a video, image or music file → enter a title, number of tokens and description;
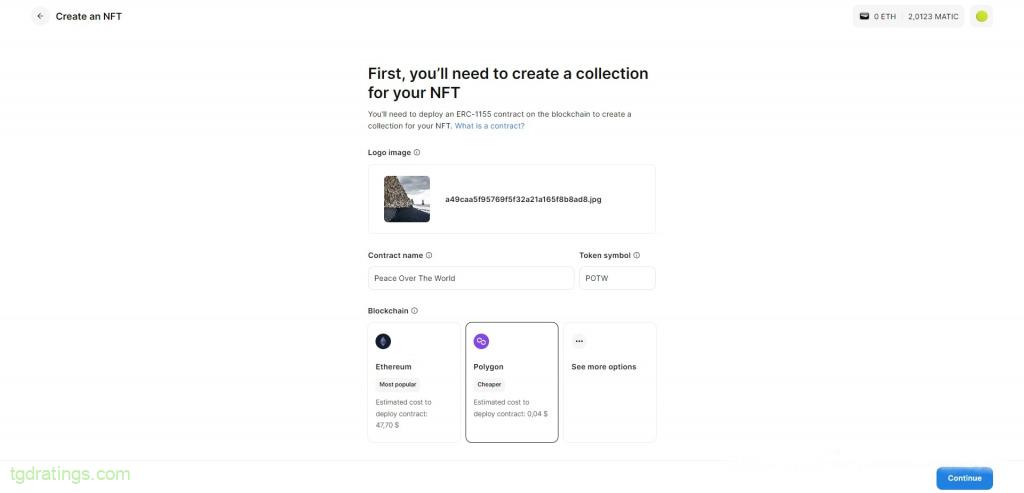
Creating NFT - Click Create a new Collection → enter the name of the collection and add an image to its avatar → select Polygon as the network for minting → Continue → pay for the creation of the collection in your wallet;
Creating a collection - Check the information in the NFT creation window → click Create → confirm payment.
3. Sell NFT
Once the NFT is created, you can sell it on the marketplace. The process looks like:
- Once the first NFT is ready, OpenSea will offer to put it up for sale. To do this, click List Item;
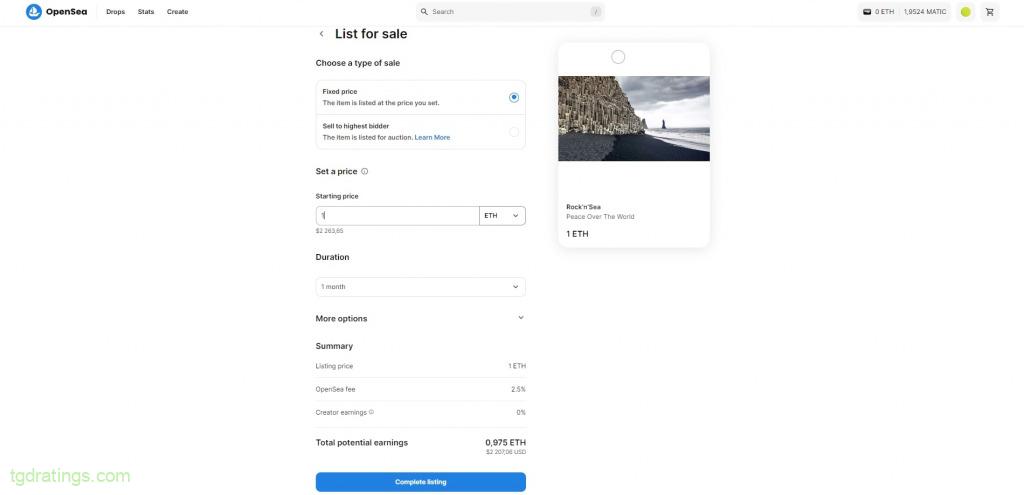
Screen with an offer - Select a pricing option (Fixed Price – set price, Sell to highest bidder – auction), enter the starting price, time to sell the token → Complete listing.
Filling selling order
Risks and Сriticism of NFTs
The main criticism of NFTs focused on issues of eco-friendliness of non-fungible tokens, some unresolved copyright issues, and high financial risks.
Environmental Concerns
One of the main complaints about NFTs is their environmental footprint. Tokens created on high-power networks (typically PoW blockchains) are very expensive in terms of electricity costs. The more electricity needed, the more fossil fuels need to be burned. Creating NFTs in this sense is considered not the most rational way to use resources. On the other hand, most NFTs are created on the Ethereum network, and after its transition to PoS, this issue is no longer so pressing.
Copyright Issues
Copyright is a complex area that varies widely from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. The issue of NFT authorship is clearly resolved thanks to a unique signature, but using the token after the sale involves many nuances. For example, can the new owner of an NFT use it commercially without paying royalties or commissions?
Some of these issues are already being resolved. For example, by adding an algorithm to the smart contract of the token, which transfers a certain percentage of coins to the author (royalty) from each resale of the token. However, there are no generally accepted solutions on this issue yet.
Financial Risks
Due to the high market volatility and speculative interest in NFTs, you can easily lose money (especially during the hype market stage). Unfortunately, there are many cases where users have bought NFTs for millions, only to have their price drop to just a few dollars. When buying well-known or new NFTs, you should always carefully study both the project itself and pay attention to the news background around it.
Conclusion
NFTs are non-fungible tokens with a digital signature, which makes them unique and indivisibility. Most often, with the help of such tokens, objects of digital painting, music, small videos, manuscripts, books, documents or game objects of metaverses and GameFi projects are digitized. Any Internet user can make their own token: just create a crypto wallet, create some valuable asset, go to the NFT marketplace and mint a token. Although there is a lot of money to be made from NFT tokens, this market is considered to be highly volatile and very risky. The most expensive NFT token is the Merge piece by artist Pak, sold in 2021 on the Nifty Gateway platform for $91.8 million.
FAQ